Torsten Zuberbier, Luis Felipe Ensina, Ana Giménez-Arnau, et al. (2024) The Lancet. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00852-3.
Summary
 |
| Available and novel therapies under development for chronic urticaria |
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
Torsten Zuberbier, Luis Felipe Ensina, Ana Giménez-Arnau, et al. (2024) The Lancet. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00852-3.
Summary
 |
| Available and novel therapies under development for chronic urticaria |
Yamana, Y., Yamana, S. & Uchio, E. Sci Rep 14, 16235 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-67117-3
Abstract
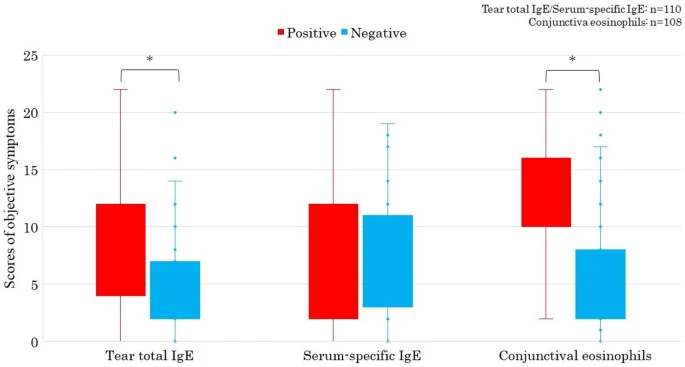 |
| Comparison of objective symptoms’ scores by JACQLQ ver1 between cases positive or negative for tear total IgE, serum specific IgE and conjunctival eosinophils |
Emilio Narváez-Fernández, Margarita Tomás-Perez. EMJ Allergy Immunol. 2024;9[1]:63-69.
Abstract
Introduction: Eosinophilic oesophagitis (EoE) is an emerging disease of the oesophagus. However, so far there are no fully validated biomarkers for diagnosis and monitoring. Moreover, research focuses on parameters that are not very useful and accessible for routine clinical practice. Thus, endoscopy remains the main method of follow-up in this population.
Methods: The team analysed the levels of total Ig E, absolute eosinophil count (AEC), eosinophil cationic protein, and immunoglobulin G4 in a cohort of 399 adult patients with EoE (without other oesophageal pathologies). After controlling for confounding factors, they compared patients with active EoE and those in remission (responders).
 |
| Comparison of markers by treatment group. |
Abstract
Allergic diseases are showing increasing prevalence in Western societies. They are characterized by a heightened reactivity towards otherwise harmless environmental stimuli. Allergic diseases showing a wide range of severity of symptoms have a significant impact on the quality of life of affected individuals. This study aims to highlight the mechanisms that induce these reactions, how they progress, and which prenatal factors influence their development. Most frequently, the reaction is mediated by immunoglobulin E (IgE) produced by B cells, which binds to the surface of mast cells and basophils and triggers an inflammatory response. The antibody response is triggered by a shift in T-cell immune response. The symptoms often start in early childhood with eczema or atopic dermatitis and progress to allergic asthma in adolescence.
 |
| Environmental, epigenetic and genetic factors leading to the development of allergic diseases |
Abstract
Background
Current treat-to-target recommendations for atopic dermatitis (AD) may not include high enough treatment targets and do not fully consider patient needs.
Objective
To develop recommendations for optimized AD management, including disease severity assessments, treatment goals and targets, and guidance for treatment escalation/modification.
Methods
An international group of expert dermatologists drafted a series of recommendations for AD management using insights from a global patient study and 87 expert dermatologists from 44 countries. Experts voted on recommendations using a modified eDelphi voting process.
Results
 |
| Overview of the AHEAD approach. |
Abstract
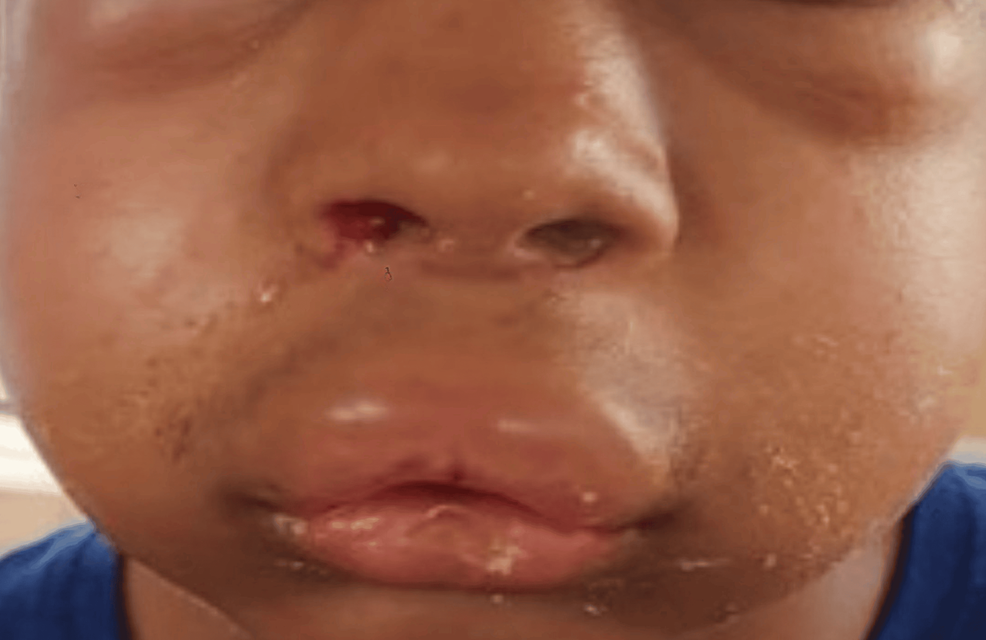 |
| Diclofenac-induced hypersensitivity reaction - angioedema |
Abstract
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a prevalent inflammatory disorder of the nasal mucosa, triggered by allergen exposure and characterized by symptoms such as sneezing, nasal congestion, itching, and rhinorrhea. This comprehensive review aims to unravel the molecular mechanisms underpinning AR, exploring the pathogenesis from allergen recognition to chronic inflammation and tissue remodelling. Central to the disease are immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated hypersensitivity reactions, involving key inflammatory mediators and cellular players such as mast cells, eosinophils, and T cells.
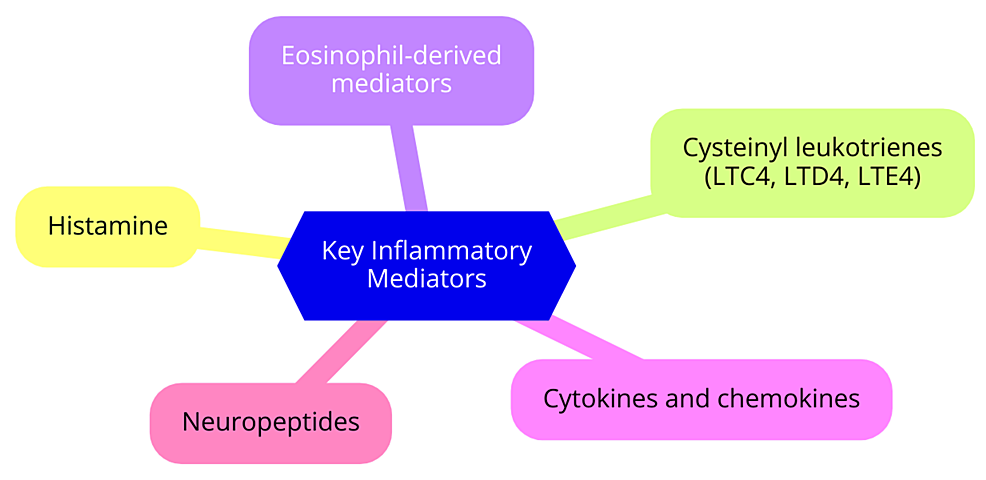 |
| Key inflammatory mediators involved |