Di Bona D, Paoletti G, Cognet-Sicé J et al. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 2025; Vol 35(5) : 341-352 doi: 10.18176/jiaci.1076
Abstract:
 |
| Subgroup analyses of symptom score by age and sensitization status of sublingual immunotherapy vs placebo. |
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
Di Bona D, Paoletti G, Cognet-Sicé J et al. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 2025; Vol 35(5) : 341-352 doi: 10.18176/jiaci.1076
Abstract:
 |
| Subgroup analyses of symptom score by age and sensitization status of sublingual immunotherapy vs placebo. |
Beiner, L., Boehm, I. Insights Imaging 16, 216 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13244-025-02099-y
Abstract
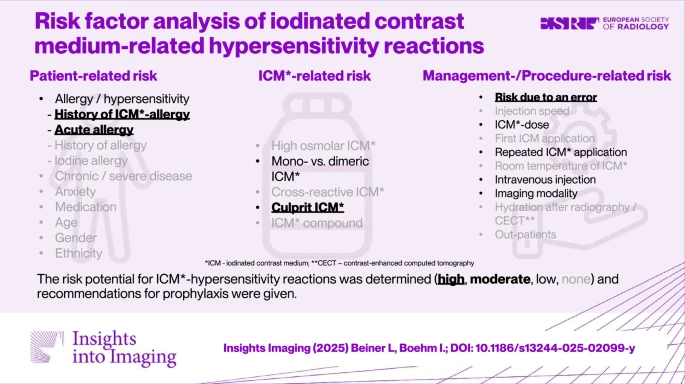 |
| Graphical Abstract |
Abstract
Background:
Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), allergic rhinitis (AR), and asthma are common airway disorders that often coexist, suggesting shared inflammatory mechanisms. LPR involves gastric reflux into the laryngopharynx, while AR and asthma are linked by the “united airway” hypothesis. Evidence indicates LPR may contribute to AR and asthma exacerbation, yet their interactions remain unclear. Understanding their interaction may enhance clinical outcomes.
Objective:
This systematic review aimed to evaluate the associations between LPR, AR, and asthma by analyzing studies that examined these conditions in various patient populations.
Methodology:
Jean Bousquet:
Bernardo Sousa-Pinto:
Tanninen TH, Reiterä PH, Saarto A et al. Clin Transl Allergy. 2025 Oct;15(10):e70101. doi: 10.1002/clt2.70101.
ABSTRACT
Background
Mobile health (mHealth) applications for asthma and allergic rhinitis (AR) may guide patients in following medication use, symptoms, and lung function supporting self-management.
Objective
The primary study objective was to investigate the objective effect of birch pollen on asthma and AR symptoms and medicine use in pediatric patients with varying levels of birch-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) during the 2022 birch pollen season using digital tools. The secondary objectives were to determine the effect of birch pollen on Asthma Control Test scores, and to record the subjective benefits in self-management while using the application.
Methods
Altogether, 48 pediatric participants were categorized into three groups based on their birch-specific IgE levels.
Dungan, L., Cox, F. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 21, 43 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-025-00972-5
Abstract
Background
Hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media (ICM) are rare but can be life-threatening. Management typically involves avoidance of the offending agent and the use of alternative imaging strategies. The phenomenon of a transient refractory period—wherein a patient does not exhibit an allergic response upon re-exposure to the allergen shortly after an initial reaction—has been proposed but is not well-documented in the context of ICM.
Case presentation
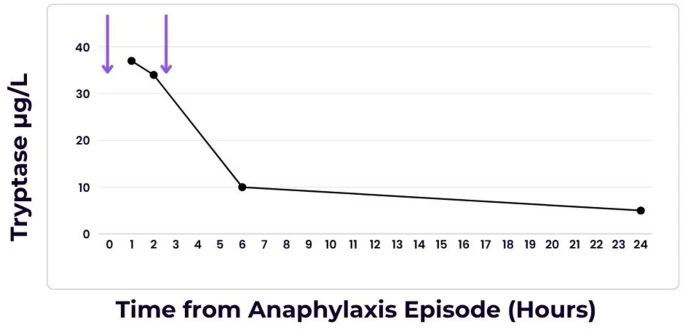 |
| Serum Tryptase versus Time from Anaphylaxis Episode. Purple arrows represent the two time points at which iodinated contrast media was administered. |
Abstract
Purpose of Review
Food allergy is a significant public health problem, affecting 8% of children and 3–4% of adults, with potentially life-threatening anaphylaxis being its most severe manifestation. Trigger food avoidance is still the mainstay of food allergy management, while novel treatments, including specific allergen immunotherapy and omalizumab, a humanized IgG1κ antibody, have shown potential to reduce the risk of allergic reaction after food ingestion. The purpose of this review is to provide an account of current knowledge regarding efficacy and safety profile of omalizumab in the management of food allergy, implemented as a standalone treatment or in combination with oral immunotherapy of food allergy.
Recent Findings
 |
| Food protein threshold values after OMA or placebo treatment |