- Case Report
- Open Access
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology 18, Article number: 18 (2022)
Abstract
Background
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is characterized by a necrotizing vasculitis with tissue and peripheral blood eosinophilia affecting small and medium-sized arteries, capillaries, and veins. Venous thromboembolic events are uncommon in EGPA. Moreover, there are only a few reported cases of EGPA complicated by pulmonary embolism or infarction.
Case presentation
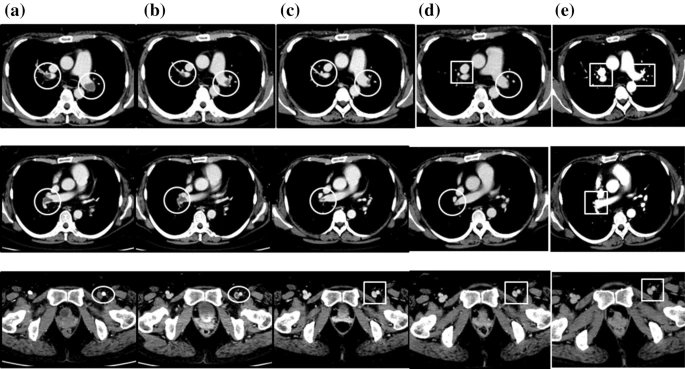
We report the case of a 43-year-old woman with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis and acute respiratory and heart failure due to bilateral pulmonary artery thrombosis and left femoral vein thrombosis 12 years after disease onset. She also had cardiac involvement (myocarditis, pericardial effusion, and diastolic dysfunction), gastrointestinal symptoms, and peripheral neuropathy. The condition was refractory to treatment with systemic corticosteroids, intravenous cyclophosphamide, and mepolizumab, but the thrombosis and associated acute cardiac failure, as well as the cardiac and gastrointestinal symptoms and multiple polyneuropathy, improved after a switch to rituximab. However, the heart failure did not improve sufficiently and the patient continued to need inhaled oxygen at 1 L/min and asthma exacerbations occurred. We then swapped the patient’s mepolizumab treatment for dupilumab. Not only did she have no further asthma attacks after switching to dupilumab, but also her vasculitis symptoms improved. Oxygen therapy was discontinued as the heart failure improved 5 months after starting the dupilumab.Conclusions
This may be the first case report of the successful treatment by rituximab of pulmonary thromboembolism associated with EGPA. In addition, in this patient, treatment with dupilumab was effective not only for the asthma symptoms but also for the symptoms of vasculitis and heart failure.
No comments:
Post a Comment