Untaaveesup, S., Amnartpanich, T., Leelakanok, N. et al. Sci Rep 15, 9009 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-86779-1
Abstract
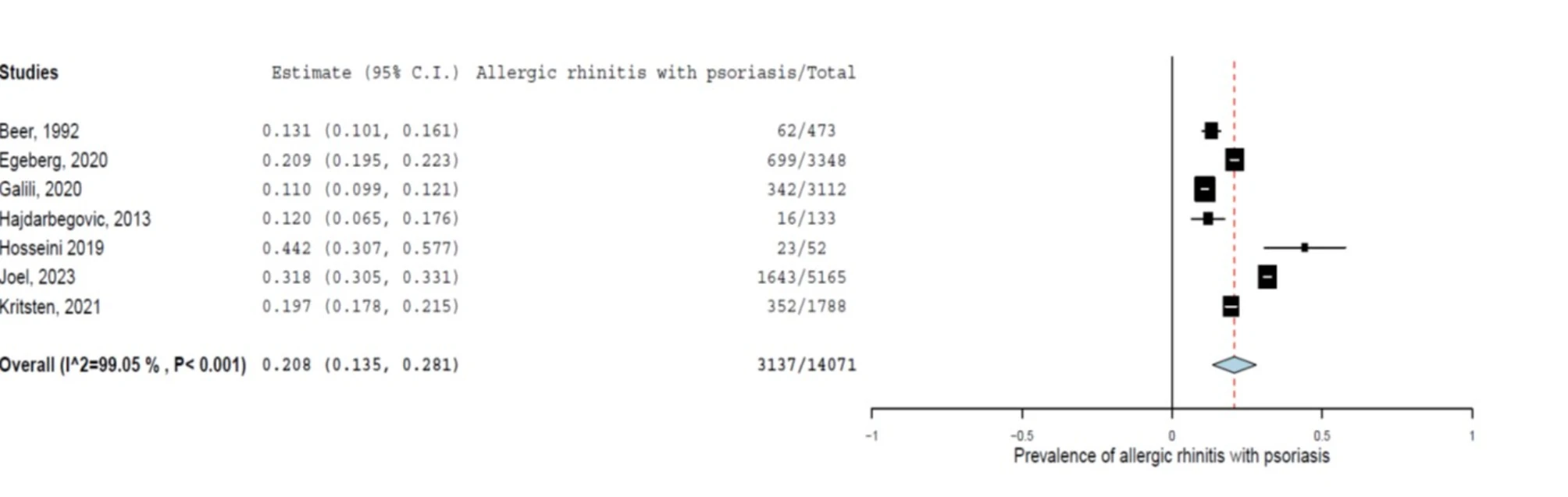 |
| A pooled prevalence of allergic rhinitis in patients with psoriasis |
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
Untaaveesup, S., Amnartpanich, T., Leelakanok, N. et al. Sci Rep 15, 9009 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-86779-1
Abstract
 |
| A pooled prevalence of allergic rhinitis in patients with psoriasis |
No comments:
Post a Comment