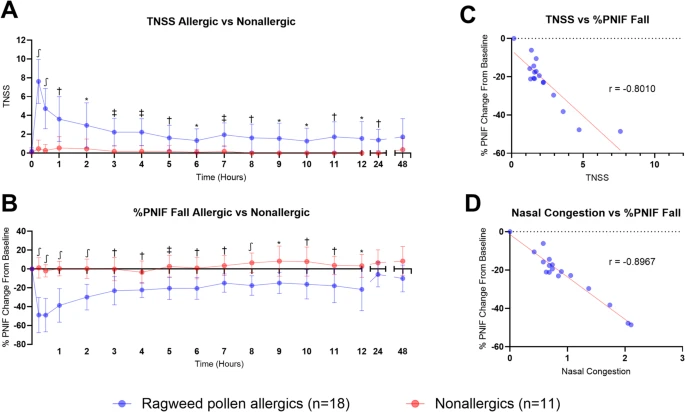
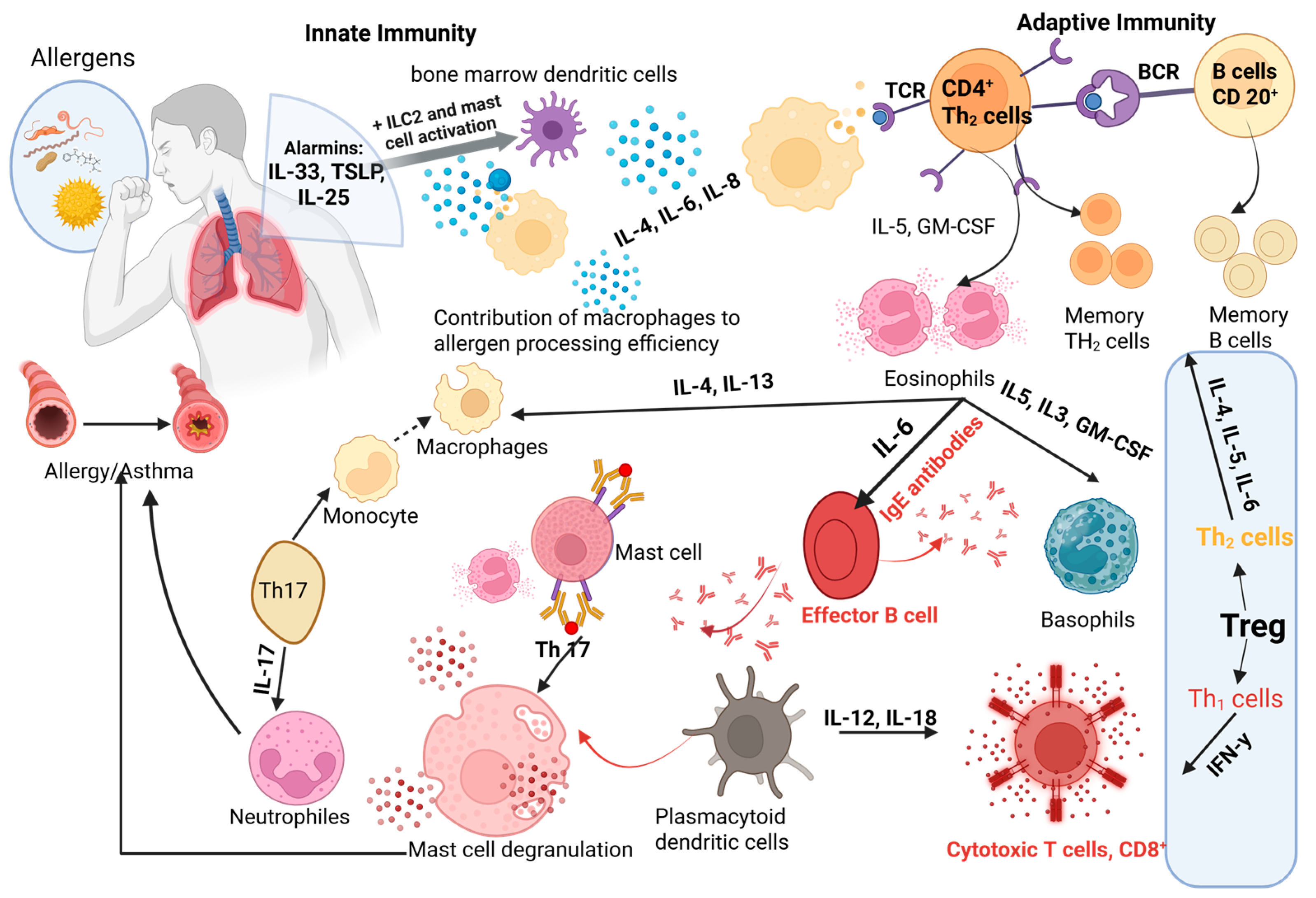
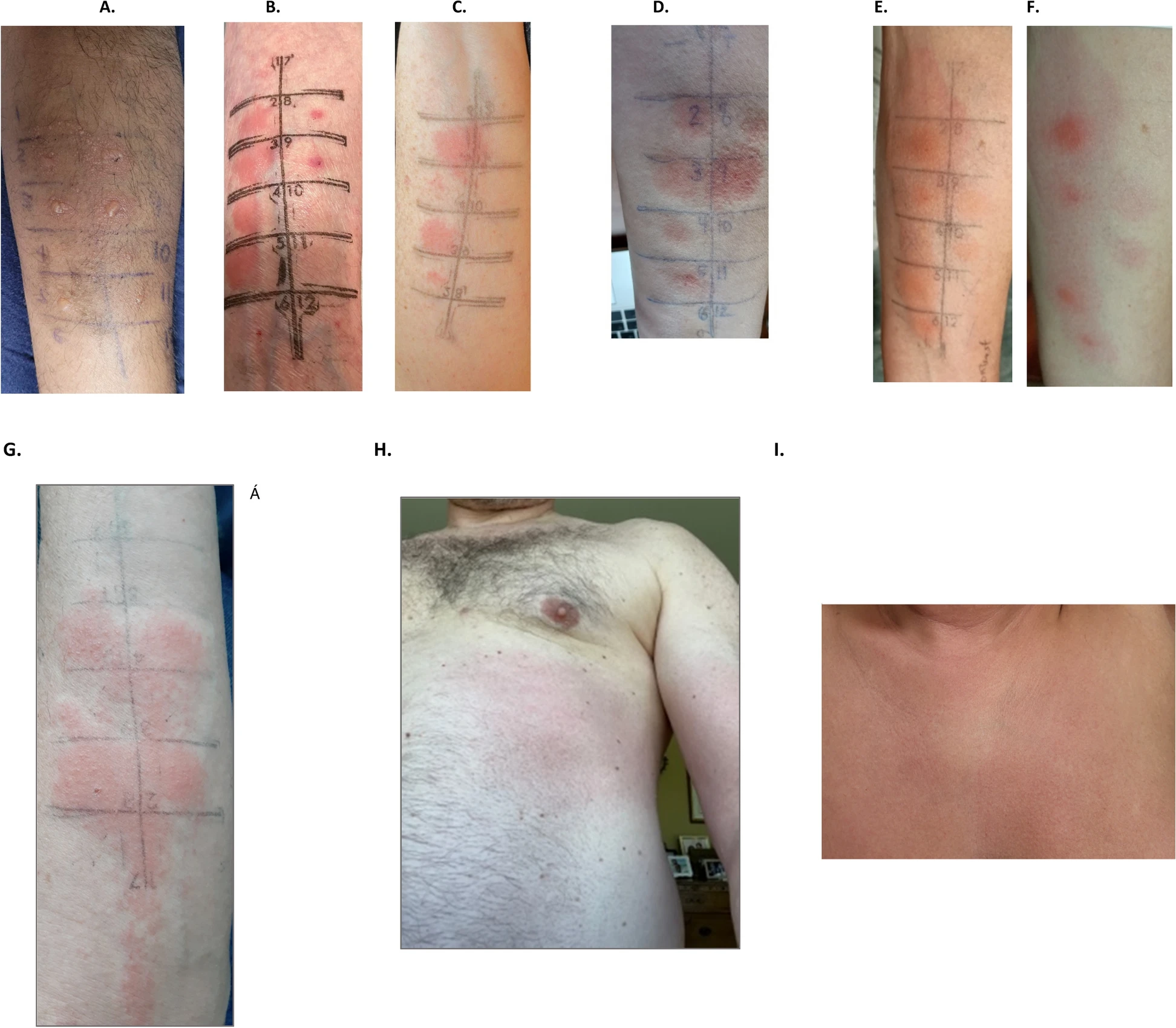
Sabouraud-Leclerc, D., Mariotte, D., Bradatan, E., Divaret-Chauveau, A., Metz-Favre, C., Beaumont, P., Dumond, P., Serrier, J., Karaca-Altintas, Y., Tscheiller, S., Pouessel, G. and Van der Brempt, X. (2025), Clin Exp Allergy. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.70130ABSTRACT
Background
The European Regulation list on mandatory labelling of foods includes 14 allergenic foods; however, other foods are also frequently implicated in food-induced anaphylaxis (FIA).
Methods
We analysed FIA cases reported to the Allergy Vigilance Network from 2002 to 2023. Allergenic foods involved in ≥ 1% of cases and not included in the list were assessed as emerging food allergens (EFA). We assessed their frequency, severity (Ring classification), recurrence, and potential presence in hidden form to determine which allergens might warrant inclusion on the list.
Results