Abstract:
 |
| After injection, urticaria-like manifestations occurred on the upper face, with redness, swelling, and wheal formation. |
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
Abstract:
 |
| After injection, urticaria-like manifestations occurred on the upper face, with redness, swelling, and wheal formation. |
ABSTRACT
Background
An allergen exposure chamber (AEC) is a specialized medical facility designed to expose individuals to allergens at precise and consistent concentrations within a controlled environment. This study aimed to correlate the assessment of clinical endpoints in patients with allergic rhinitis sensitized to timothy grass pollen (Phleum pratense) by comparing three different methods: AEC, nasal allergen challenge (NAC), and symptoms during natural exposure during the grass pollen season.
Methods
Fifteen allergic subjects and twelve healthy controls were evaluated in the ALLEC AEC; allergic symptoms were measured by subjective and objective methods, including total nasal symptom score (TNSS), acoustic rhinometry (AcR), peak nasal inspiratory flow (PNIF), and nasal discharge amount.
Abstract
Food allergy has had a rapid rise in prevalence, and thus it is important to identify approaches to limit the development of food allergy early in life. Because maternal dietary supplementation with α-tocopherol (α-T), an isoform of vitamin E, during pregnancy and nursing increases neonate plasma levels of α-T and can limit neonate development of other allergies, we hypothesized that α-T can limit development of food allergy. To assess this, male mice with mutations in their skin barrier genes (FT−/− mice) were mated with wild-type females that received a diet supplemented with α-tocopherol or a control diet. Starting at postnatal day 3, these FT+/− pups were sensitized 4 to 5 times over 2.5 weeks by skin co-exposure to the food allergen peanut extract (PNE) and the environmental allergen Alternaria alternata (Alt). Control pups were exposed to saline, PNE only or Alt only. Supplementation with α-T blocked Alt+PNE sensitization (anti-PNE-specific IgE), without blocking Alt+PNE-stimulated skin IL33, Areg, OSM, CCL11, TSLP or plasma MCPT1.
Untaaveesup, S., Amnartpanich, T., Leelakanok, N. et al. Sci Rep 15, 9009 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-86779-1
Abstract
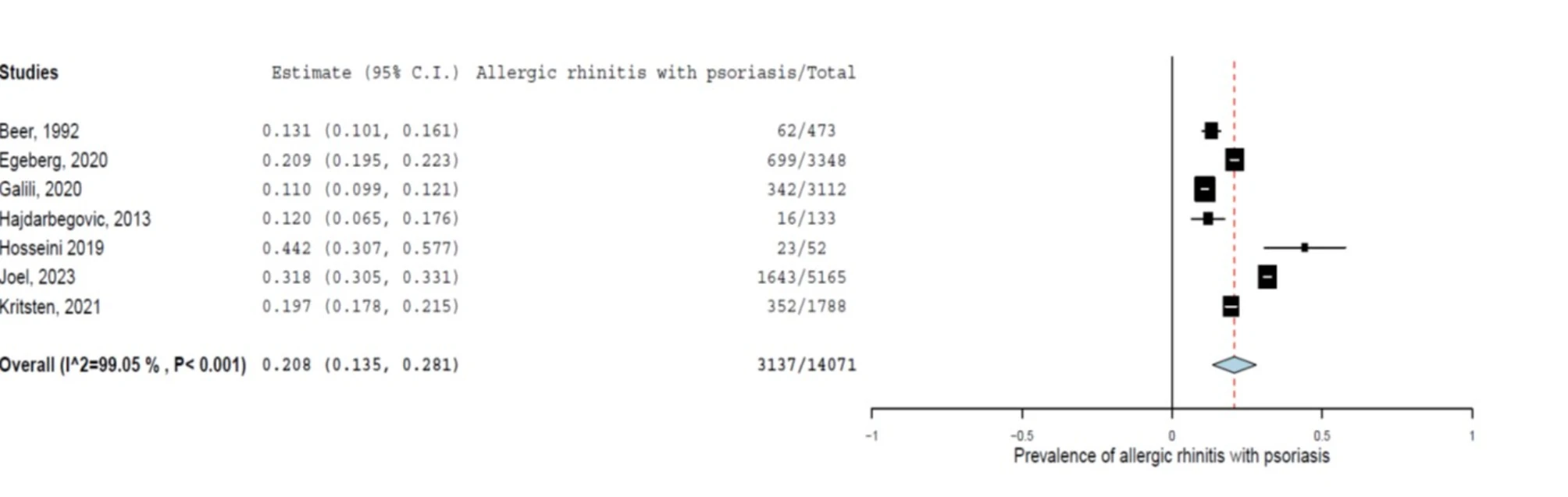 |
| A pooled prevalence of allergic rhinitis in patients with psoriasis |
Portela D, Freitas A, Costa E, Giovannini M, Bousquet J, Almeida Fonseca J, Sousa-Pinto B. J Med Internet Res. 2025 Mar 10;27:e51804. doi: 10.2196/51804.
Abstract
Background:
Google Trends (GT) data have shown promising results as a complementary tool to classical surveillance approaches. However, GT data are not necessarily provided by a representative sample of patients and may be skewed toward demographic and clinical groups that are more likely to use the internet to search for their health.
Objective:
In this study, we aimed to assess whether GT-based models perform differently in distinct population subgroups. To assess that, we analyzed a case study on asthma hospitalizations.
Methods:
We analyzed all hospitalizations with a main diagnosis of asthma occurring in 3 different countries (Portugal, Spain, and Brazil) for a period of approximately 5 years (January 1, 2012-December 17, 2016).
Ren, F., Zhang, L., Zhao, D. et al. BMC Pulm Med 25, 109 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-025-03523-1
Abstract
Background
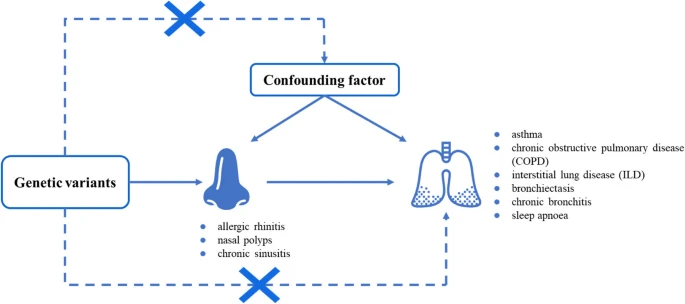 |
| Schematic representation of Mendelian randomization on the relationship between nasal disease and chronic respiratory diseases |
Methods
In this study, a two-sample mendelian randomization was employed to explore the potential association between allergic rhinitis, nasal polyps, and chronic sinusitis with various chronic respiratory diseases.
Abstract
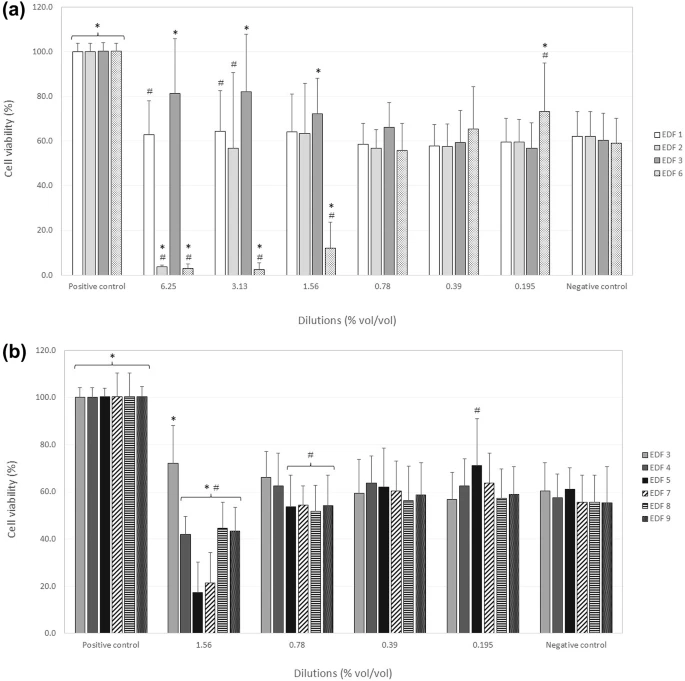 |
| Quantitative determination of the protective effect of selected antiallergic aye drop formulations against dehydration in Human Primary Conjunctival Epithelial Cells (HConEpiC) |