Ali, A., Alamri, A., Mishra, V.K. et al. BMC Immunol (2026). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12865-025-00795-4
Abstract
 |
| Graphical Abstract |
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
Ali, A., Alamri, A., Mishra, V.K. et al. BMC Immunol (2026). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12865-025-00795-4
 |
| Graphical Abstract |
 |
| Visual Summary |
Aparicio E E, Guerrero D V, Alcántara V D, et al. (December 26, 2025) Cureus 17(12): e100143. doi:10.7759/cureus.100143
Abstract
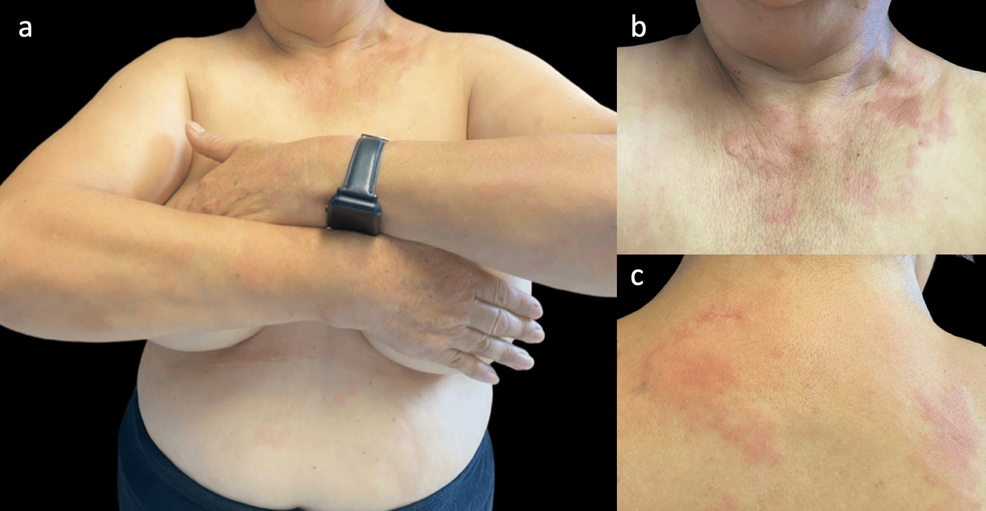 |
| Cutaneous manifestations of hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis |
Rossi CM, Terreehorst I, Apostolidou E et al. Allergy. 2025 Dec 16. doi: 10.1111/all.70183.
ABSTRACT
 |
| Risk of bias (RoB) domains for the randomized controlled trials (RCT) on the development of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) after allergen immunotherapy (AIT). |
Singh AK, Shaili S, Siddiqui A et al. Front Allergy. 2025 Dec 4;6:1636415. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2025.1636415.
Abstract
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a complex, multifactorial condition that continues to pose significant clinical and public health challenges, despite the availability of established therapeutic strategies. It significantly contributes to a lower quality of life by causing sleep issues, mental fatigue, and a decline in productivity. A thorough grasp of AR is crucial to enhancing diagnosis and treatment results because of its pervasive effects and ongoing management gaps. This review covers a wide range of topics, such as classification schemes, historical perception, and physical consequences of AR.
 |
| Forest plot depicting reduction in UAS7 compared to placebo at week 12 of dupilumab 300 mg biweekly, omalizumab 300 mg, 150 mg, or 75 mg every four weeks, and remibrutinib 25 mg twice daily. |
Zhang, YY., Lu, MP., Chen, YB. et al. Sci Rep (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-31902-5
Abstract
| The impacts of allergic rhinitis (AR) and allergen-specific sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have not been fully understood. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the effects of AR and SLIT on symptoms of COVID-19 within one month after Chinese authorities adjusted their COVID-19 response measures. The study enrolled 1368 participants, including 746 AR patients and 622 controls without allergic diseases. SLIT was administered to 122 infected AR patients (AR with SLIT group), while it was not administered to the other 483 infected AR patients (AR without SLIT group). Patients’ outcomes were compared after propensity score matching (PSM). The data showed that AR played a dual role in COVID-19, acting as both a protective factor against respiratory symptoms and a risk factor increasing the likelihood of olfactory/gustatory dysfunctions and fever, compared to non-allergic individuals. |
Jabagi M, Bertrand M, Gabet A et al. JAMA. Published online December 22, 2025. doi:10.1001/jama.2025.24082
Key Points
Importance Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a leading cause of hospitalization in infants. The comparative effectiveness of 2 recently introduced preventive strategies (infant immunization through placental antibody transfer after maternal vaccination with the RSV prefusion F protein [RSVpreF] vaccine and passive infant immunization with nirsevimab) remains unknown.
Objective To compare the associations of maternal vaccination with the RSVpreF vaccine vs passive infant immunization with nirsevimab for the prevention of RSV-related hospitalization.
Design, Setting, and Participants This population-based cohort study used data from the French National Health Data System. Maternal vaccination with the RSVpreF vaccine occurred during 32 to 36 weeks’ gestation among infants born in mainland France between September 1 and December 31, 2024. Passive infant immunization with nirsevimab occurred prior to hospital discharge. Infants were matched 1:1 by maternity ward discharge date, sex, gestational age, and region. Follow-up ended at the time of RSV hospitalization or death or on February 28, 2025.
Exposures Maternal immunization with the RSVpreF vaccine and passive infant immunization with nirsevimab.
Main Outcomes and Measures The primary outcome was hospitalization for RSV-associated lower respiratory tract infection. The secondary outcomes included admission to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU), admission to high-dependency unit, ventilator support, and oxygen therapy. The hazard ratios (HRs) were estimated using conditional Cox proportional hazards models with inverse probability of treatment weighting.
 |
| Comparative Analysis for Primary Outcome of Hospitalization for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)–Associated Lower Respiratory Tract Infection and Secondary Outcomes Among Matched Infants |